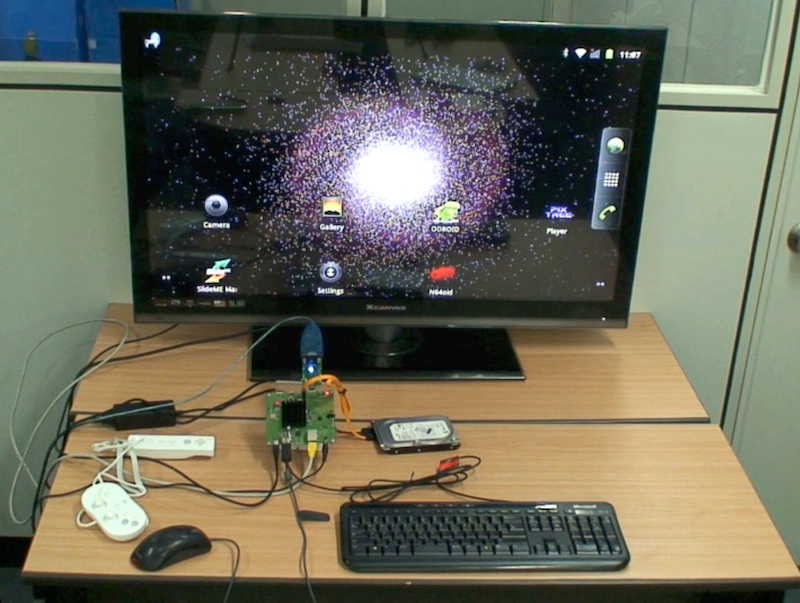
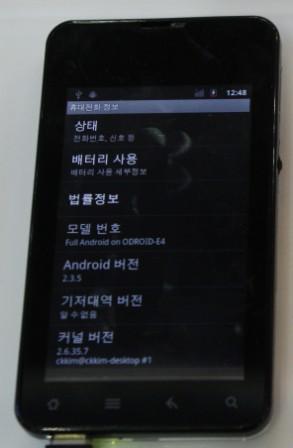
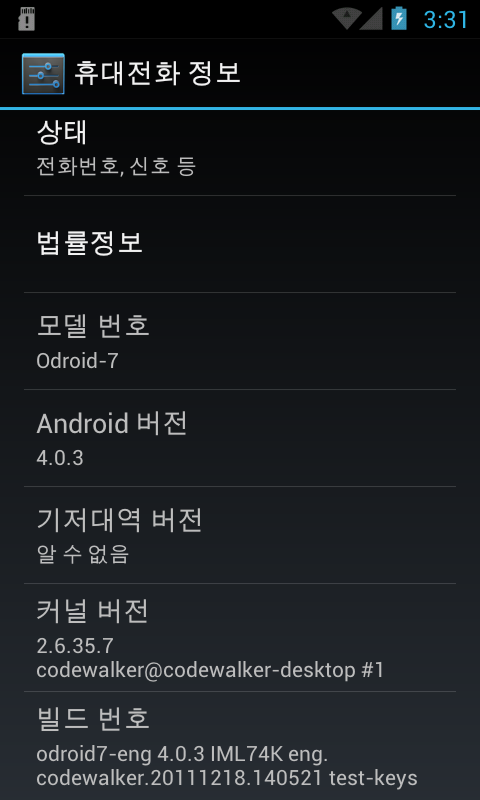
Screenshot of ICS 4.0.3 version information on ODROID-7.
Here is a brief instruction how to port/install the ICS into ODROID-7.
Note, this is a very early version. Unstable and there are many unsupported features.
1. Get the Kernel source code of ODROID-7 (ver 2.6.35)
http://com.odroid.com/sigong/nf_file_board/nfile_board_view.php?keyword=&bid=41
Modify the touch screen driver as below.
kernel/drivers/input/touchscreen/odroid7_MT_touch_portrait.c
169 input_sync(hkc1xx_touch.driver);
170
171 //codewalker
172 input_mt_sync(hkc1xx_touch.driver);
173
174 input_sync(hkc1xx_touch.driver);
175
176
177 #if defined(DEBUG_HKC1XX_TOUCH_MSG)
178 printk("%s : Penup event send[x = %d, y = %d]n", __FUNCTION__, hkc1xx_touch.x, hkc1xx_touch.y);
179 #endif
2. Download GPU device driver source code of Nexus-S from this link.
https://github.com/Kwiboo/kernel_samsung_crespo/tree/master/drivers/gpu
Copy(overwrite) the GPU code to ODROID-7 kernel source and compile it.
3. Get the official Android ICS source code.(android-4.0.3_r1 IML74K)
repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest -b android-4.0.3_r1
repo sync
4. Get the modified files from below link and overwrite it into /device & /vendor directory of ICS source tree.
http://dl.dropbox.com/u/4485660/ICS.tar.gz
This file contains various patches.
4. Get the modified files from below link and overwrite it into /device & /vendor directory of ICS source tree.
http://dl.dropbox.com/u/4485660/ICS.tar.gz
This file contains various patches.
5. Modify WiFi code as below for internet access.
device/hardkernel/odroid7/BoardConfigCommon.mk
71 #WIFI_DRIVER_MODULE_ARG := "firmware_path=/vendor/firmware/fw_bcm4329.bin nvram_path=/vendor/firmware/nvram_net.txt iface_name=wlan" 72 WIFI_DRIVER_MODULE_ARG := "iface_name=wlan firmware_path=/vendor/firmware/fw_bcm4329.bin nvram_path=/vendor/firmware/nvram"
And copy the fw_bcm4329.bin & nvram into proper location.
Modify hardware/libhardware_legacy/wifi/wifi.c
#define WIFI_WAKEUP_CTL_FP "/sys/devices/platform/hkc1xx-sysfs/wifi_wakeup" // 1 -> wakeup on
#define WIFI_REG_CTL_FP "/sys/devices/platform/hkc1xx-sysfs/wifi_reg" // 1 -> reg on
#define WIFI_RESET_CTL_FP "/sys/devices/platform/hkc1xx-sysfs/wifi_reset" // 1 -> reset on
int wifi_set_module_status (char *ctl_fp, unsigned char status);
int wifi_get_module_status (char *ctl_fp);
static int insmod(const char *filename, const char *args) {
int wifi_load_driver() { #ifdef WIFI_DRIVER_MODULE_PATH char driver_status[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX]; int count = 100; /* wait at most 20 seconds for completion */ if (is_wifi_driver_loaded()) { return 0; } // Wifi power control & wakeup enable wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_WAKEUP_CTL_FP, 1); usleep(10000); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_REG_CTL_FP, 1); usleep(10000); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_RESET_CTL_FP, 1); sleep(1); sync(); if (insmod(DRIVER_MODULE_PATH, DRIVER_MODULE_ARG) < 0) { LOGE("insmod(DRIVER_MODULE_PATH = %s, DRIVER_MODULE_ARG = %s) FAIL!!!", DRIVER_MODULE_PATH, DRIVER_MODULE_ARG); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_WAKEUP_CTL_FP, 0); usleep(10000); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_REG_CTL_FP, 0); usleep(10000); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_RESET_CTL_FP, 0); sleep(1); sync(); return -1; } if (strcmp(FIRMWARE_LOADER,"") == 0) { int wifi_unload_driver() { usleep(200000); /* allow to finish interface down */ #ifdef WIFI_DRIVER_MODULE_PATH if (rmmod(DRIVER_MODULE_NAME) == 0) { int count = 20; /* wait at most 10 seconds for completion */ while (count-- > 0) { if (!is_wifi_driver_loaded()) break; usleep(500000); } wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_WAKEUP_CTL_FP, 0); usleep(10000); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_REG_CTL_FP, 0); usleep(10000); wifi_set_module_status(WIFI_RESET_CTL_FP, 0); sleep(1); sync(); usleep(500000); /* allow card removal */ if (count) { return 0;
int wifi_set_module_status(char *ctl_fp, unsigned char status) { int fd, ret, nwr; char buf[10]; if((fd = open(ctl_fp, O_RDWR)) < 0) { LOGE("%s(%s) : Cannot access "%s"", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, ctl_fp); return -1; // fd open fail } memset((void *)buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf)); if(status) nwr = sprintf(buf, "%dn", 1); else nwr = sprintf(buf, "%dn", 0); ret = write(fd, buf, nwr); close(fd); if(ret == nwr) { LOGI("%s : write success (on = %d)", ctl_fp, status); return 0; } else { LOGE("%s : write fail (on = %d)", ctl_fp, status); return -1; } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- int wifi_get_module_status(char *ctl_fp) { int fd, ret, nrd; char buf[10]; if((fd = open(ctl_fp, O_RDONLY)) < 0) { LOGE("%s(%s) : Cannot access "%s"", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, ctl_fp); return -1; // fd open fail } memset((void *)buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf)); nrd = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); close(fd); // read ok if(nrd) { if(!strncmp(buf, "1", 1)) { LOGI("%s : status == 1", ctl_fp); return 1; // wakeup } else { LOGI("%s : status == 0", ctl_fp); return 0; // suspend } } LOGI("%s(%s) : module status == unknown", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__); return -1; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- int wifi_module_wakeup_status() { int fd, ret, nrd; char buf[10]; if((fd = open(WIFI_WAKEUP_CTL_FP, O_RDONLY)) < 0) { LOGE("%s(%s) : Cannot access "%s"", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, WIFI_WAKEUP_CTL_FP); return -1; // fd open fail } memset((void *)buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf)); nrd = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); close(fd); // read ok if(nrd) { if(!strncmp(buf, "1", 1)) { LOGI("%s(%s) : module status == wakeup", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__); return 1; // wakeup } else { LOGI("%s(%s) : module status == suspend", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__); return 0; // suspend } } LOGI("%s(%s) : module status == unknown", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__); return -1; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- int wifi_module_wait_time(int waitTime) { LOGI("%s(%s) : module wait time = %d sec", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, waitTime); sleep(waitTime); sync(); return 0; }
chmod u+x device/hardkerenl/odroid7/build_android.sh
device/hardkerenl/odroid7/build_android.sh
7. Install the Android system files and zImage and ramdisk-uboot.img as we do for Gingerbread installation.
http://dev.odroid.com/projects/odroid-t/
Tested features
– LCD driver with 3D accelerator
– Capacitive touch screen
– Sound output
– Sound input (Microphone)
– USB ADB driver
– USB Host HID (Mouse/Keyboard)
– WiFi
– MFC driver for media player
– GPS driver
– Accelerometer sensor
– HOME key function
– Backlight Brightness control
– Battery Gauge / Charger driver
To do list
– Camera
– Bluetooth
– HDMI
– Geo Magnetic Field sensor
– NFC
Update!
Modified DPI for tablet mode (density=120)
Softkey enabled
Enabled Home screen rotation


 한국어
한국어